How To Change Camera Size In Blender
A camera is an object that provides a means of rendering images from Blender. It defines which portion of a scene is visible in the rendered image.
Cameras are invisible in renders, so they do not have whatever material or texture settings. However, they practise have Object and Editing setting panels available which are displayed when a photographic camera is the active object.
Properties
Reference
- Way
-
Object Mode
- Editor
Lens
Blazon
The camera lens options control the style 3D objects are represented in a 2d prototype.
- Perspective
-
This matches how you view things in the real world. Objects in the distance volition announced smaller than objects in the foreground, and parallel lines (such as the rail on a railroad) volition appear to converge as they get farther away.
- Focal Length/Field of View
-
The Focal Length controls the corporeality of zoom, i.east. the amount of the scene which is visible all at once. Longer focal lengths result in a smaller FOV (more zoom), while short focal lengths allow you to see more of the scene at once (larger FOV, less zoom).
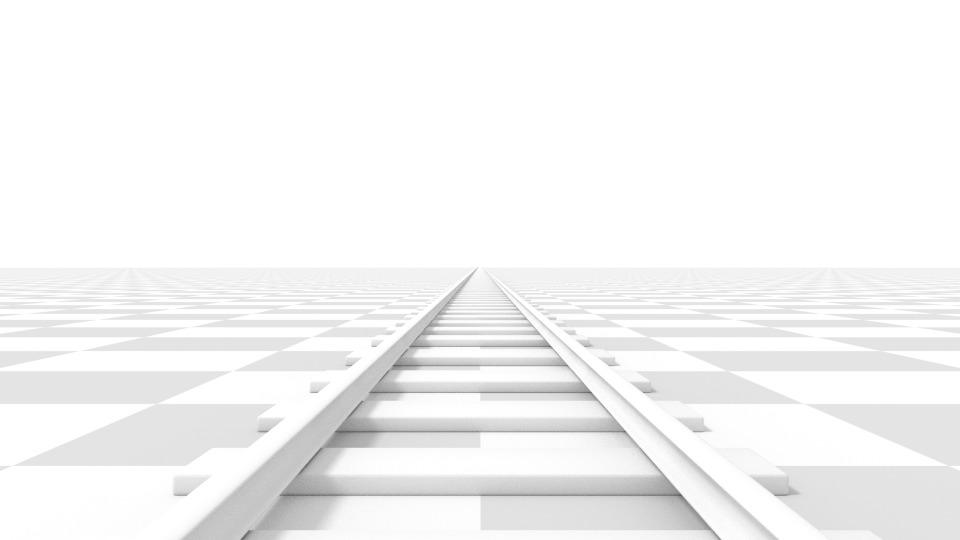

Perspective photographic camera with 35 mm focal length.
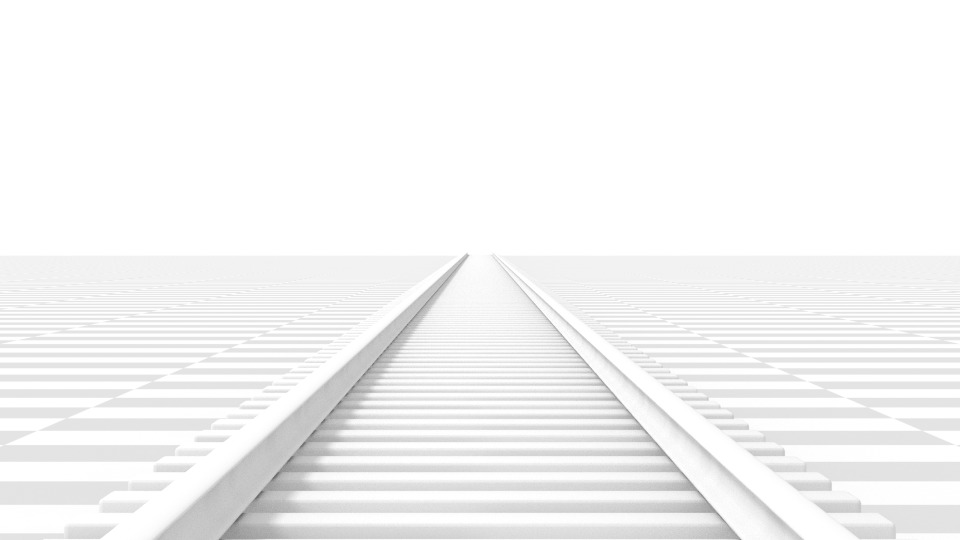

Perspective photographic camera with 210 mm focal length instead of 35 mm.
- Lens Unit
-
The focal length can be set either in terms of millimeters or the bodily Field of View as an angle.
Hint
While the camera is moving towards an object the Focal Length holding can exist decreased to produce a Dolly Zoom camera upshot, or vice versa.
This video demonstrates the Dolly Zoom camera effect.
- Orthographic
-
With Orthographic perspective objects always appear at their actual size, regardless of distance. This means that parallel lines appear parallel, and practice not converge like they exercise with Perspective.

Render from the same camera angle equally the previous examples, but with orthographic perspective.
- Orthographic Scale
-
This controls the apparent size of objects projected on the image.
Note that this is effectively the only setting which applies to orthographic perspective. Since parallel lines practise not converge in orthographic mode (no vanishing points), the lens shift settings are equivalent to translating the camera in the 3D Viewport.
- Panoramic
-
Panoramic cameras only work in Cycles. See the Cycles panoramic camera settings for more information.
- Shift
-
Allows for the adjustment of vanishing points. Vanishing points refer to the positions to which parallel lines converge. In these render examples, the most obvious vanishing point is at the end of the railroad.
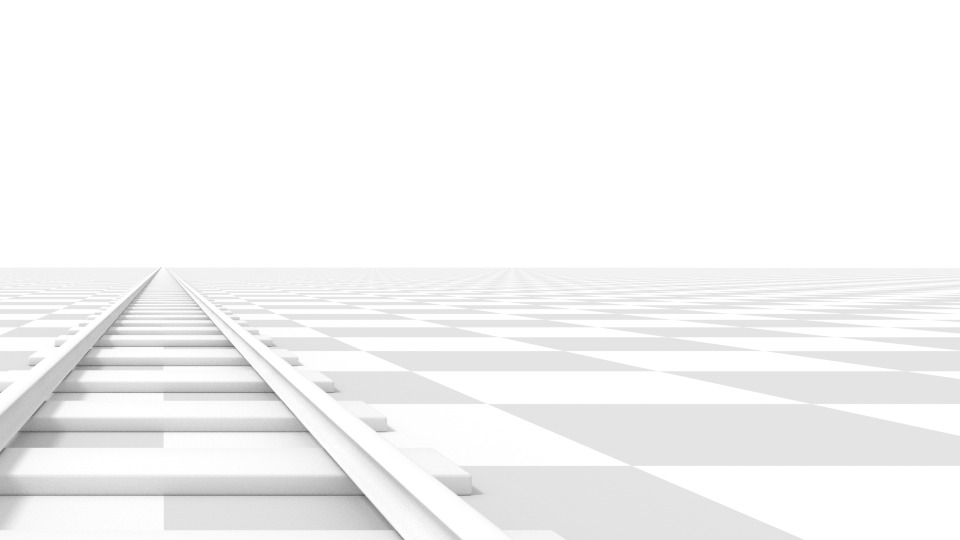

Horizontal lens shift of 0.330.
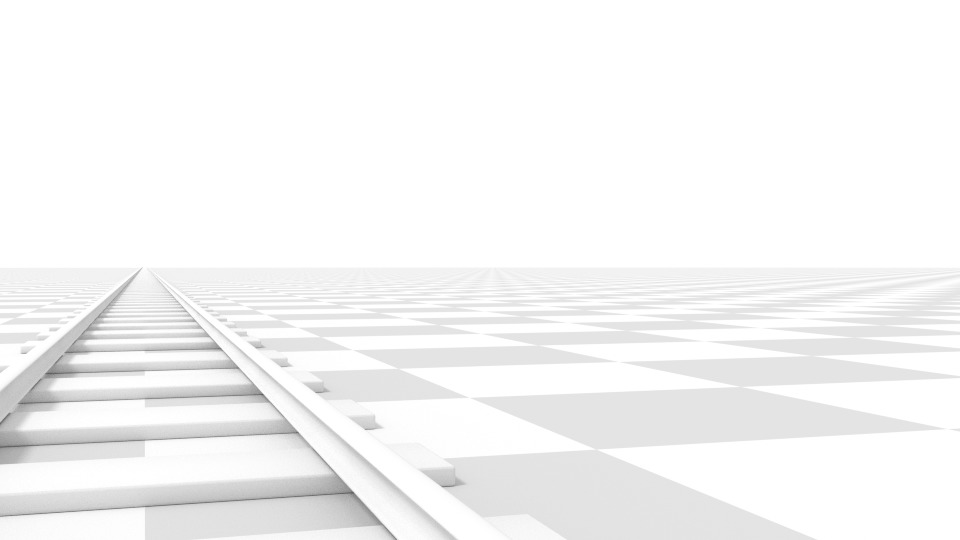

Rotation of the camera object instead of a lens shift.
Notice how the horizontal lines remain perfectly horizontal when using the lens shift, but do become skewed when rotating the camera object.
Note
Using lens shift is equivalent to rendering an paradigm with a larger FOV and cropping it off-centre.
- Clip Start and End
-
The interval in which objects are directly visible. Any objects exterior this range still influence the image indirectly, as further light bounces are non clipped.
Note
For viewport rendering, setting clipping distances to limited values is important to ensure sufficient rasterization precision. Ray tracing renders practice not endure from this issue so much, and as such more farthermost values can safely be set.
Tip
When Limits in the Viewport Display panel is enabled, the clip bounds will be visible every bit two yellow continued dots on the camera's line of sight.
Depth of Field
Real-globe cameras transmit light through a lens that bends and focuses it onto the sensor. Because of this, objects that are a certain distance away are in focus, but objects in front and behind that are blurred.
Example of DOF bokeh issue.
The area in focus is called the focal point and can be set using either an exact value, or by using the distance between the photographic camera and a chosen object:
- Focus Object
-
Choose an object which will determine the focal signal. Linking an object will conciliate the distance parameter.
- Focal Altitude
-
Sets the distance to the focal point when no Focus Object is specified. If Limits are enabled, a yellow cross is shown on the camera line of sight at this distance.
Hint
Hover the mouse over the Distance property and press E to apply a special Depth Picker. And then click on a point in the 3D Viewport to sample the distance from that point to the camera.
Aperture
- F-Stop
-
F-Stop ratio that defines the amount of blurring. Lower values give a strong depth of field effect.
- Blades
-
Total number of polygonal blades used to modify the shape of the blurred objects in the render, and render preview. As with the viewport, the minimum corporeality of blades to enable the bokeh effect is 3, resulting in a triangular-shaped blur.
- Rotation
-
Rotate the polygonal blades along the facing axis, and will rotate in a clockwise, and counter-clockwise manner.
- Ratio
-
Modify the amount of distortion to simulate the anamorphic bokeh event. A setting of 1.0 shows no distortion, where a number below i.0 volition cause a horizontal distortion, and a higher number volition cause a vertical baloney.
Camera
These settings adjusts properties that relate to a physical camera trunk. Several Presets tin can be called to match real-earth cameras.
- Sensor Fit
-
Adjusts how the camera'due south sensor fits within the outputs dimension adjusting the angular field of view.
- Auto
-
Calculates a foursquare sensor size based on the larger of the Resolution dimensions.
- Horizontal
-
Manually accommodate the Width of the sensor, the Height is calculated based on the attribute ratio of the output's Resolution.
- Vertical
-
Manually suit the Top of the sensor, the Width is calculated based on the aspect ratio of the output's Resolution.
- Size / Width, Peak
-
This setting is an culling way to control the field of view, every bit opposed to modifying the focal length. It is useful to lucifer a photographic camera in Blender to a physical camera and lens combination, e.thou. for motion tracking.
Condom Areas
Safe areas are guides used to position elements to ensure that the most of import parts of the content tin can be seen beyond all screens.
Different screens have varying amounts of Overscan (particularly older Boob tube sets). That means that non all content will be visible to all viewers, since parts of the image surrounding the edges are not shown. To work effectually this problem TV producers defined two areas where content is guaranteed to be shown: activeness safe and championship safe.
Modern LCD/plasma screens with purely digital signals have no Overscan, yet safe areas are yet considered best do and may be legally required for circulate.
In Blender, safe areas can exist set from the Photographic camera and Sequencer views.

Red line: Action condom. Green line: Title safe.
The Safety Areas can be customized by their outer margin, which is a pct scale of the expanse betwixt the center and the render size. Values are shared between the Video Sequence editor and camera view.
- Title Safe Margins Ten/Y
-
Besides known as Graphics Safe. Place all of import information (graphics or text) inside this area to ensure it can exist seen past the majority of viewers.
- Action Safe Margins X/Y
-
Brand certain any significant action or characters in the shot are inside this area. This zone likewise doubles as a sort of "margin" for the screen which tin can be used to keep elements from piling upward confronting the edges.
Tip
Each land sets a legal standard for dissemination. These include, among other things, specific values for safe areas. Blender defaults for rubber areas follow the EBU (European Matrimony) standard. Brand sure you are using the correct values when working for broadcast to avoid any trouble.
Center-Cutting Safe Areas
Center-cuts are a second prepare of safety areas to ensure content is seen correctly on screens with a different attribute ratio. Old TV sets receiving 16:9 or 21:9 video will cut off the sides. Position content inside the heart-cut areas to make certain the near important elements of your limerick tin still be visible in these screens.
Blender defaults prove a 4:3 (foursquare) ratio inside 16:9 (widescreen).
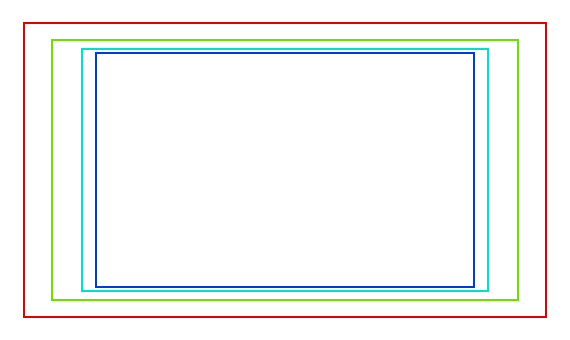
Cyan line: action center condom. Blue line: championship heart safe.
Background Images
A background picture in your camera can be very helpful in many situations: modeling is apparently one, but it is also useful when painting (e.k. y'all tin have reference pictures of faces when painting textures directly on your model…), or animation (when using a video every bit groundwork), etc.
- Background Source
-
The source of the background epitome.
- Image
-
Use an external image, prototype sequence, video file or generated texture.
- Movie Prune
-
Use one of the Flick Clip data-blocks.
- Agile Clip
-
Brandish a Movie Clip from the scene's Active Clip.
- Render Undistorted
-
Display the groundwork paradigm using undistorted proxies when available.
- Proxy Render Size
-
Select between full (non-proxy) brandish or a proxy size to draw the groundwork image.
- Colour Infinite
-
The colour space the image or video file uses within Blender.
- Opacity
-
Controls the transparency of the background image.
- Depth
-
Choose whether the image is shown backside all objects, or in front of everything.
- Frame Method
-
Controls how the image is placed in the camera view.
- Stretch
-
Forces the image dimensions to match the camera bounds (may modify the aspect ratio).
- Fit
-
Scales the image down to fit inside the photographic camera view without altering the aspect ratio.
- Crop
-
Scales the epitome upward and so that information technology fills the entire photographic camera view, but without altering the aspect ratio (some of the image will exist cropped).
- Commencement 10, Y
-
Positions the background image using these offsets.
In orthographic views, this is measured in the normal scene units. In the camera view, this is measured relative to the camera bounds (0.1 will start information technology by 10% of the view width/tiptop).
- Rotation
-
Rotates the image around its heart.
- Scale
-
Scales the image upwardly or down from its center.
- Flip
-
- X
-
Swaps the image effectually, such that the left side is now on the right, and the correct now on the left.
- Y
-
Swaps the image around, such that the tiptop side is now on the lesser, and the lesser at present on the top.
Viewport Display
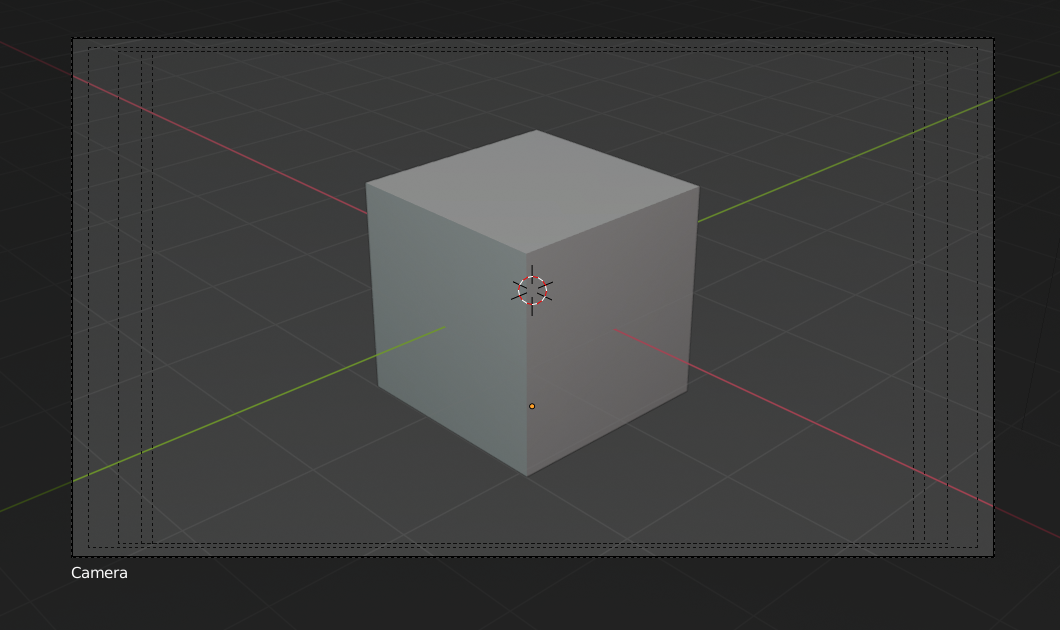
Camera view displaying safe areas, sensor and name.
- Size
-
Size of the camera visualization in the 3D Viewport. This setting has no upshot on the render output of a camera. The camera visualization tin also be scaled using the standard Scale South transform key.
- Evidence
-
- Limits
-
Shows a line which indicates Starting time and Terminate Clipping values.
- Mist
-
Toggles viewing of the mist limits on and off. The limits are shown as two connected white dots on the photographic camera line of sight. The mist limits and other options are fix in the Globe panel, in the Mist section.
- Sensor
-
Displays a dotted frame in camera view.
- Name
-
Toggle name display on and off in camera view.
Limerick Guides
Composition Guides enable overlays onto the camera display that can help when framing a shot.
- Thirds
-
Adds lines dividing the frame in thirds vertically and horizontally.
- Center
-
- Center
-
Adds lines dividing the frame in half vertically and horizontally.
- Diagonal
-
Adds lines connecting reverse corners.
- Golden
-
- Ratio
-
Divides the width and height into Gilt proportions (almost 0.618 of the size from all sides of the frame).
- Triangle A
-
Displays a diagonal line from the lower left to upper right corners, then adds perpendicular lines that pass through the top left and bottom right corners.
- Triangle B
-
Aforementioned as A, simply with the contrary corners.
- Harmony
-
- Triangle A
-
Displays a diagonal line from the lower left to upper right corners, then lines from the peak left and bottom right corners to 0.618 the lengths of the reverse side.
- Triangle B
-
Same every bit A, but with the contrary corners.
- Passepartout
-
This option darkens the area exterior of the camera'southward field of view. The opacity of the passepartout tin be adjusted using the value slider.
Source: https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/latest/render/cameras.html
Posted by: russotookents.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Change Camera Size In Blender"
Post a Comment